
Web each molecule has a different bond arrangement How does this diagram account for the.
#MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY DIAGRAM HOW TO#
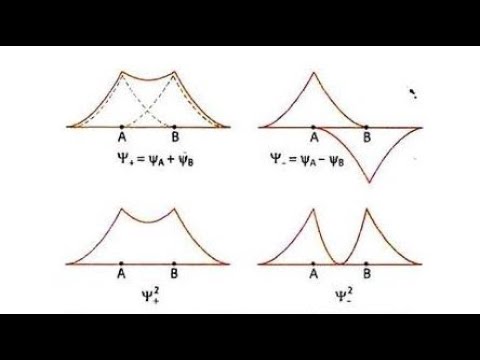
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (mo) diagram for the he2(+) ion. To further demonstrate the consistency of the Lewis structures with M.O. At first, 1s orbital of both o atom are mixed to form 1 bonding mo i.e. It has higher energy than that of atomic orbitals from which it is formed.Įlectron charge density in between the nuclei is low thus the ABMO does not favours the bond formation. The orbital correlation diagram in predicts the same thing-two electrons fill a single bonding molecular orbital. It has lower energy than that of atomic orbitals from which it is formed.Įlectron charge density in between the nuclei is high and hence the repulsion between the nuclei is very low and thus the BMO favours the stable bond formation.Īnti Bonding Molecular OrbitalAntibonding molecular orbitals are formed by the subtraction of atomic orbitals. However, for a basic diagram, we will include only the O 2p. Each pair will make the same add/subtract combinations we've seen before.
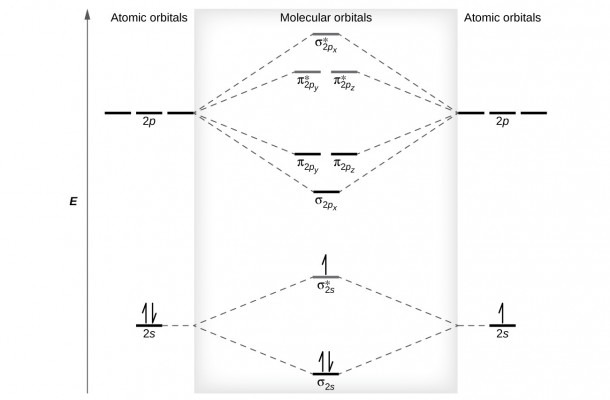
We can combine 2s orbitals, 2p x orbitals, 2p y orbitals and 2p z orbitals. Now we have to make combinations of 4 different AOs from oxygen. Chemistry Important Questions Class 12 | ExamseggBond order can easily be calculated by Moleculat Orbital Diagram by the following formula-īond Order = 1/2(Bonding Electrons − Antibonding Electrons)īonding Molecular OrbitalBonding molecular orbitals are formed by the combination of atomic orbitals. However MO theory can explain the bonding in B2H6 naturally and easily without making ad-hoc corrections. This is a little more complicated example.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
